Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) are short, synthetic, single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotides. ASOs can alter RNA and reduce, restore, or modify protein expression through several mechanisms. ASO-mediated therapies target the source of the pathogenesis, thereby having a higher chance of success than therapies targeting downstream pathways. An improved understanding of antisense pharmacology enabled the translation of these therapeutics into the clinic. Several ASO-mediated therapies have now received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration. However, enabling successful ASO therapies in the clinic requires optimizing ASO delivery, target engagement, and safety profiles.
Synthetic antisense oligonucleotides can modulate RNA function, influencing gene expression levels, exon skipping, and epitranscriptomics. However, understanding the function of various RNAs and the proteins they interact with can take time and effort.
The ASO technology can potentially change the therapeutic landscape for many neurological and non-neurological conditions soon. Antisense technology promises to deliver therapeutics for treating diseases by targeting RNA.
Modifications in approved oligonucleotide-based drugs are mainly based on a few sugar and backbone modifications. Modifications use in earlier ASO drugs are 2’-fluoro (2’-F), 2’-O-Methyl (2’-O-Me), phosphorothioate (PS) chemistries and 2’-O-methoxyethyl (2’-O-MOE) RNA and neutral phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) backbone analogs.
Bio-Synthesis offers a comprehensive suite of technologies to enable your RNA research and help you to answer these critical questions.
Selected References
ASO Insights
Egli, M., Manoharan, M.; Chemistry, structure and function of approved oligonucleotide therapeutics, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 51, Issue 6, 11 April 2023, Pages 2529–2573, NAR
Rinaldi, C., Wood, M. Antisense oligonucleotides: the next frontier for treatment of neurological disorders. Nat Rev Neurol 14, 9–21 (2018). Nature
Table 1: Approved Antisense Drugs
| Name | Category | Approval Date | Indications |
| | | | |
| Fomivirsen (Vitravene) 5'-GCGTTTGCTCTTCTTCTTGCG-3', Phosphorothioate Oligonucleotide Fomivirsen | ASO | 1998.08 | Cytomegalovirus Retinitis |
| Pegaptanib (Macugen) 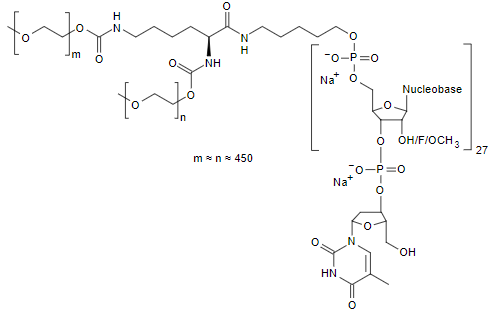 Pegaptanib Pegaptanib | Aptamer | 2004.12 | Age-Related Macular Degeneration |
| Mipomersen (Kynamro) 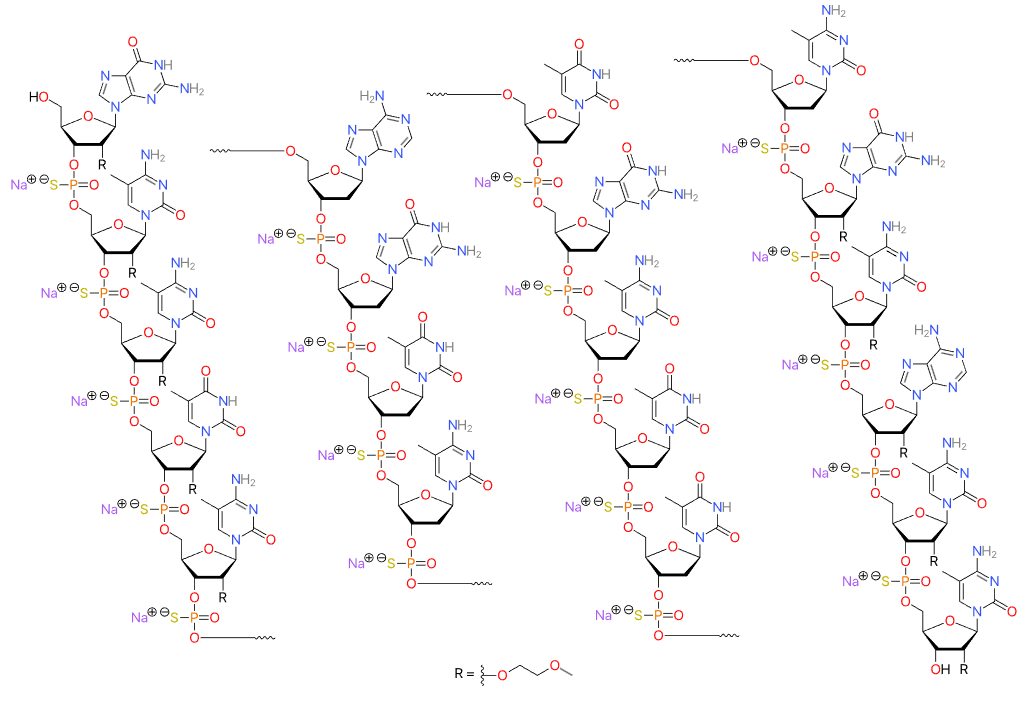 Phosphorothioate Oligonucleotide. Mipomersen | ASO | 2013.01 | Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia |
| Defibrotide (Defitelio) Deoxyribonucleic acid derivative extracted from mammalian organs. Defitelio-defibrotide-sodium | ss-DNA and ds-DNA | 2016.03 | Hepatic Veno- Occlusive Disease |
| Eteplirsen (Exondys 51) Eteplirsen is a morpholino antisense oligomer which triggers excision of exon 51 during pre-mRNA splicing of the dystrophin RNA transcript. 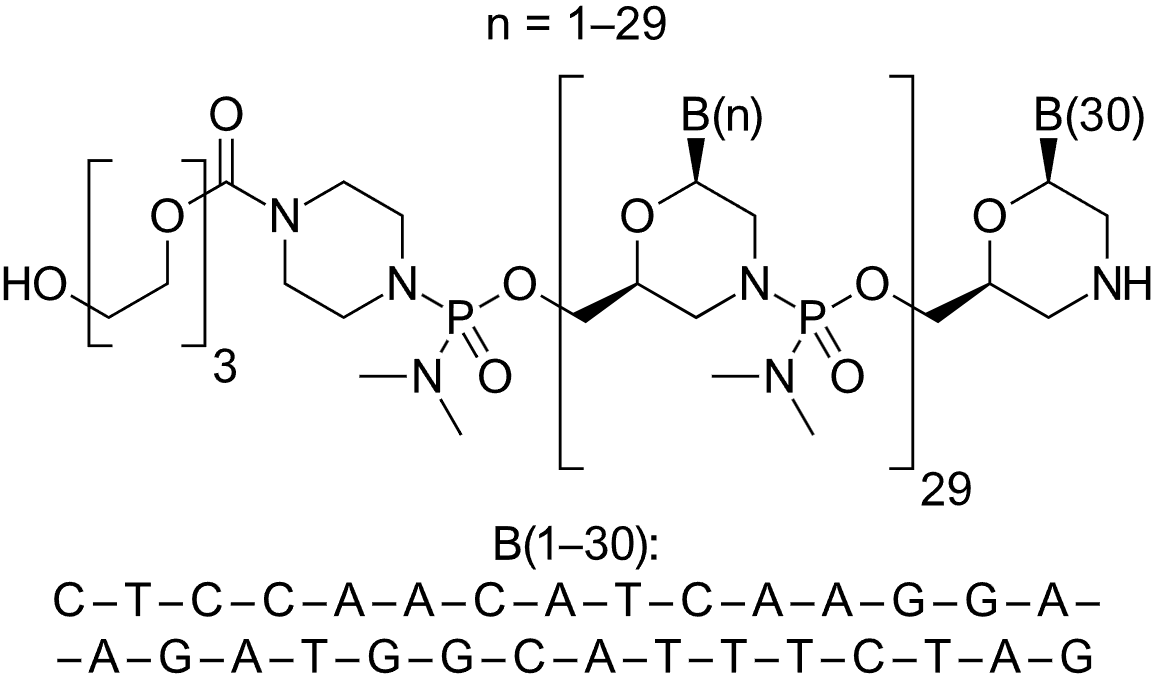 Eteplirsen | ASO Morpholino | 2016.09 | Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy |
| Nusinersen (Spinraza) 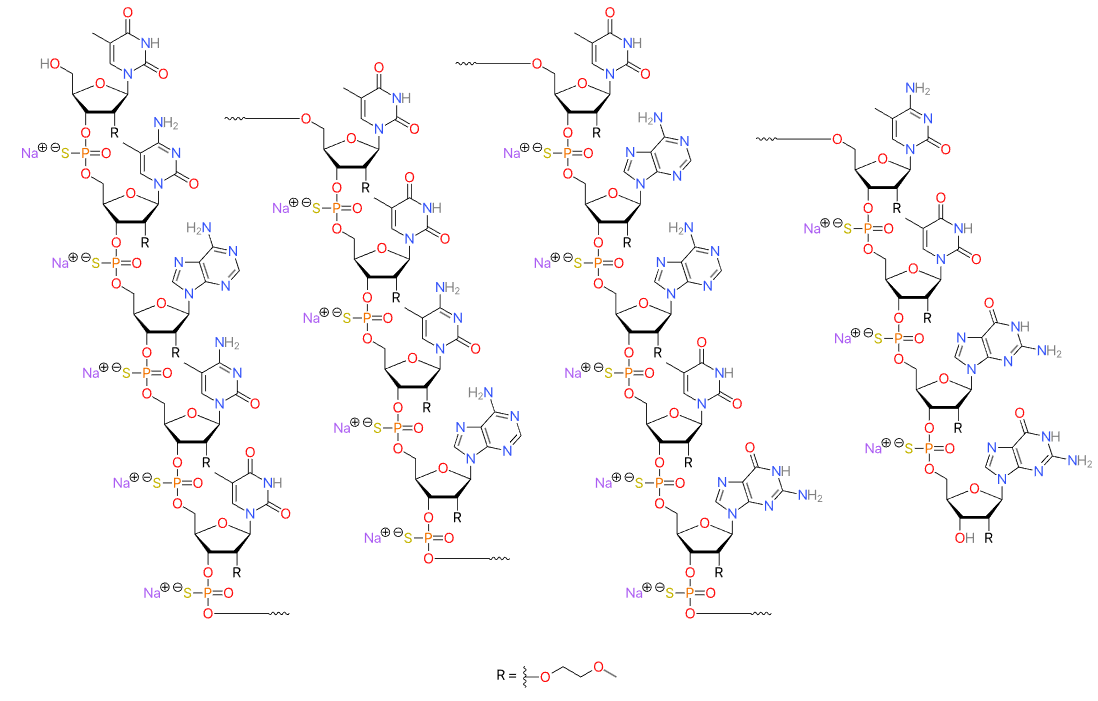 Phosphorothioate Oligonucleotide. Nusinersen | ASO | 2016.12 | Spinal Muscular Atrophy |
| HepB-CpG (HEPLISAV-B) 5’-TGACTGTGAACGTTCGAGATGA-3’ HEPLISAV-B is a hepatitis B vaccine composed of recombinant hepatitis B virus surface antigen particles (rHBsAg) mixed with a synthetic oligonucleotide containing CpG motifs that stimulate innate immunity through TLR9, containing CpG oligonucleotide as adjuvant! FDA, Heplisav, DB11627 | 22-mer PS DNA Vaccine | 2017.11 | Hepatitis B |
| Patisiran (Onpattro) 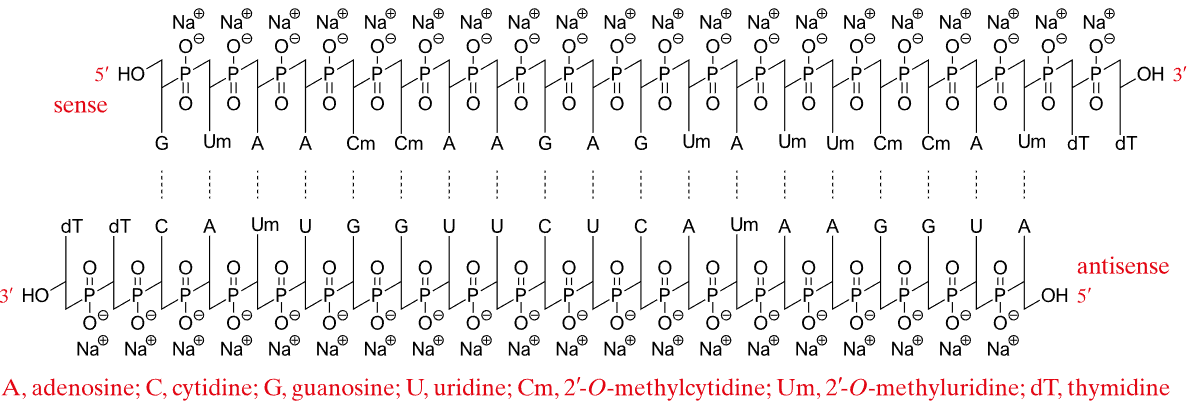 Patisiran, DB14582 | siRNA | 2018.08 | Heterotrophic Transthyretin Amyloidosis |
| Inotersen (Tegsedi) ASO with sequence TCTTG GTTACATGAA ATCCC, where C is methylated C, and the first and third section (bases 1-5 and 16–20, separated from the middle section by spaces) are MOE-modified. 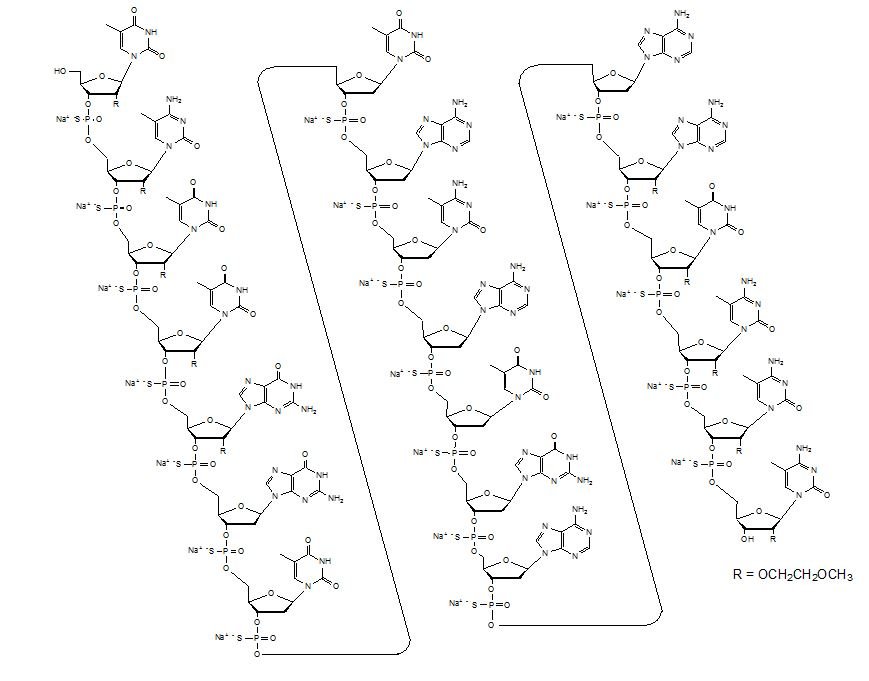 Inotersen, DB14713, Tegsedi | ASO | 2018.01 | Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis, Polyneuropathy |
| Volanesorsen (Waylivra) This triglyceride-reducing drug is a second-generation 2'-O-methoxyethyl (2'-MOE) chimeric antisense therapeutic oligonucleotide (ASO) targeting the messenger RNA for apolipoprotein C3 (apo-CIII). Sequence: 3'—A*—G*—mC*—T*—T*—dmC—dT—dT—dG—dT—dmC—dmC—dA—dG—dmC—T*—T*—T*—A*—T*—5', * = 2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl), m = 5-methyl, d = 2'-deoxy
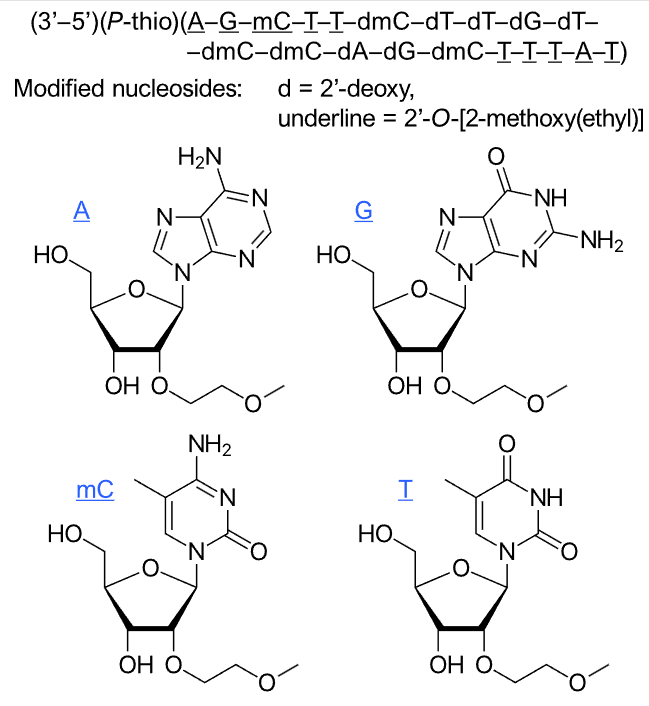 PubMed, Volanesorsen | ASO 20mer Gapmer | 2019.05 | Familial chylomicronaemia syndrome (FCS) (also known as type I hyperlipo- proteinaemia). |
| Givosiran (Givlaari) 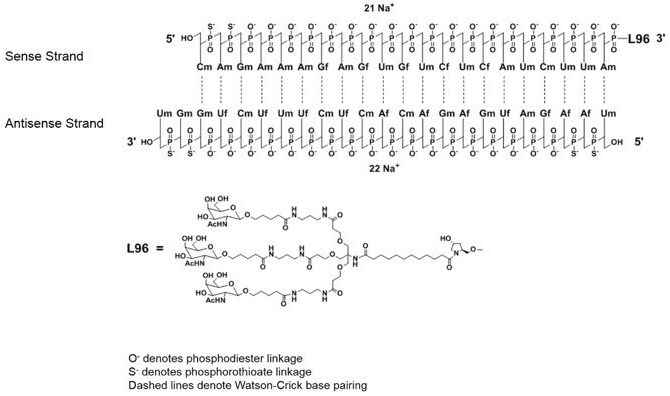
FDA, Givlaari | siRNA | 2019.11 | Acute Hepatic Porphyrias |
| Golodirsen (Vyondys 53) all-P-ambo-[2′,3′-Azanediyl-P-(dimethylamino)-P,2′,3′-trideoxy-2′,3′-seco](2′-N→5′) (G-T-T-G-C-C-T-C-C-G-G-T-T-C-T-G-A-A-G-G-T-G-T-T-C) 5′-{P-[4-({2-[2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-ethoxy]-ethoxy}-carbonyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-N,N-dimethylphosphonamidate}; Formula: C305H481N138O112P25 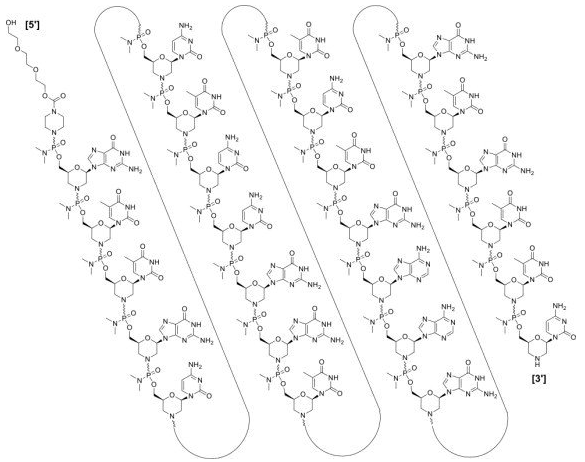 Golodirsen, Approval, DB15593, Vyondys-53, Golodirsen, Golodirsen | ASO | 2019.12 | Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy |
| Viltolarsen (Viltepso) Morpholino oligonucleotide (PMO) 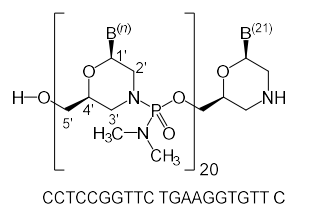 Viltolarsen, Viltepsos-mechanism-action | ASO | 2020.08 | Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy |
| Lumasiran (Oxlumo) 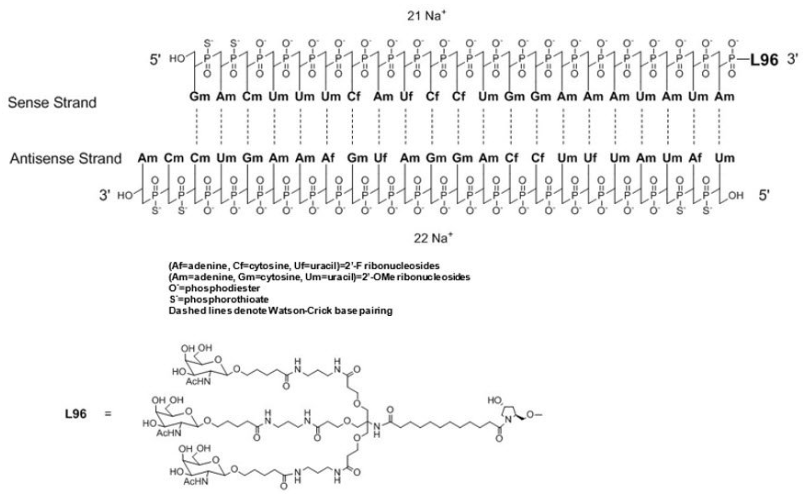 Lumasiran sodium: C530H669F10N173O320P43S6Na43, Mw 17,286 Da. Lumasiran, Drugs-trials-snapshot-oxlumo, Oxlumo-injection | siRNA | 2020.11 | Primary Hyperoxaluria Type 1 (PH1) |
| Inclisiran (LeqvioTM) 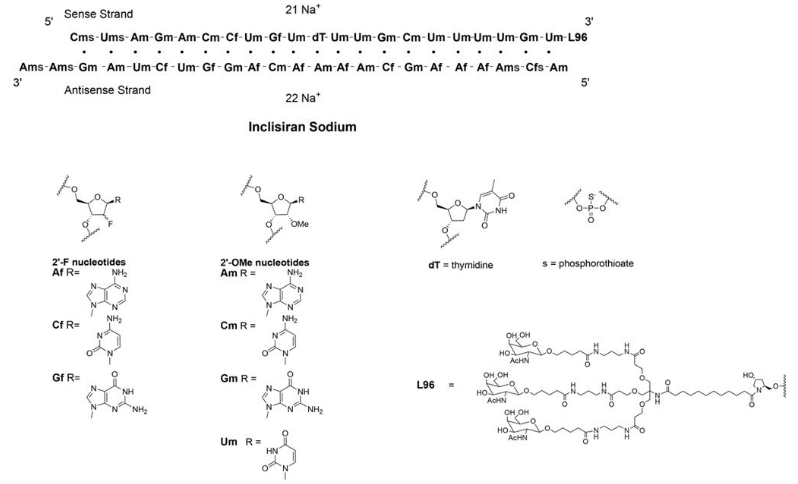 Abbreviations: Af = adenine 2'-F ribonucleotide; Cf = cytosine 2'-F ribonucleotide; Gf = guanine 2'-F ribonucleotide; Am = adenine 2'-OMe ribonucleotide; Cm = cytosine 2'-OMe ribonucleotide; Gm = guanine 2'-OMe ribonucleotide; Um = uracil 2'-OMe ribonucleotide; L96 = triantennary GalNAc (N-acetyl-galactosamine). Leqvio, Novartis-receives-eu-approval-leqvio-inclisiran | siRNA | 2021.12 | Hypercholesterolemia |
| Casimersen (Amondys 45) Sequence: 5'-CAATGCCATCCTGGAGTTCCTG-3'. C268H424N124O95P22. Mw 7584.5 daltons. 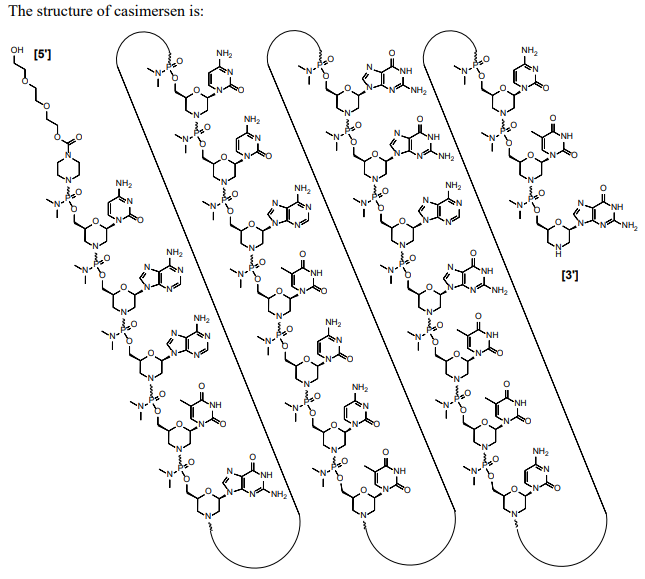 Drug-trial-snapshot-amondys-45, PMC, FDA | ASO | 2021.02 | Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy |
| Vutrisiran (Amvuttra) Medication for the treatment of the polyneuropathy of hereditary transthyretin-mediated (hATTR) amyloidosis in adults, targeting the mRNA of transthyretin. Vutrisiran sodium: C530H672F9N171Na43O323P43S6; Mw: 17,290 Da. Free acid: C530H715F9N171O323P43S6; Mw: 16,345 Da. 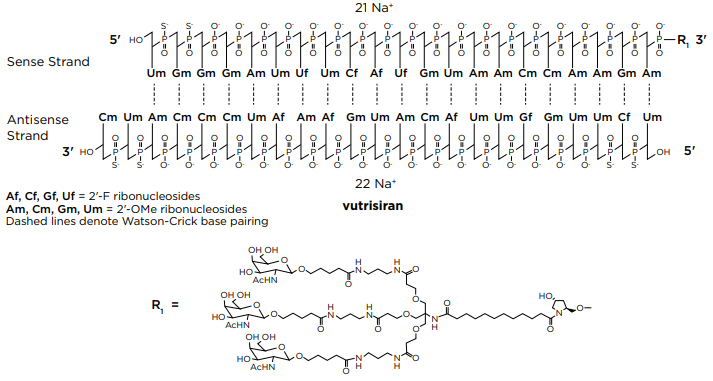 Vutrisiran, DB16699, Fda-novel-drug-approvals-june-2022/, AMVUTTRA | siRNA | 2022.06 | TTR, liver |
| Nedosiran (Rivfloza) Nedosirna sodium: C662H808F19N231O413P57S6Na57, Mw: 22,238 Da, freely soluble in water. 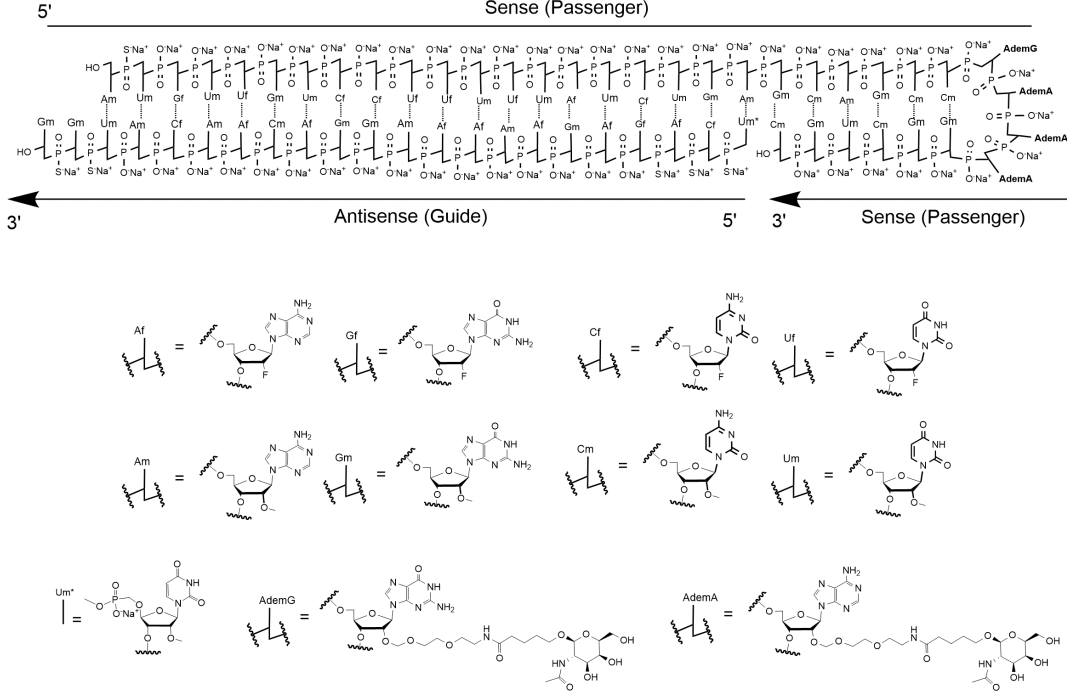 DB17635, PMC, Eplontersen, FDA | siRNA | 2023.09 | Primary Hyperoxaluria (PH) |
| Eplontersen (Wainua) 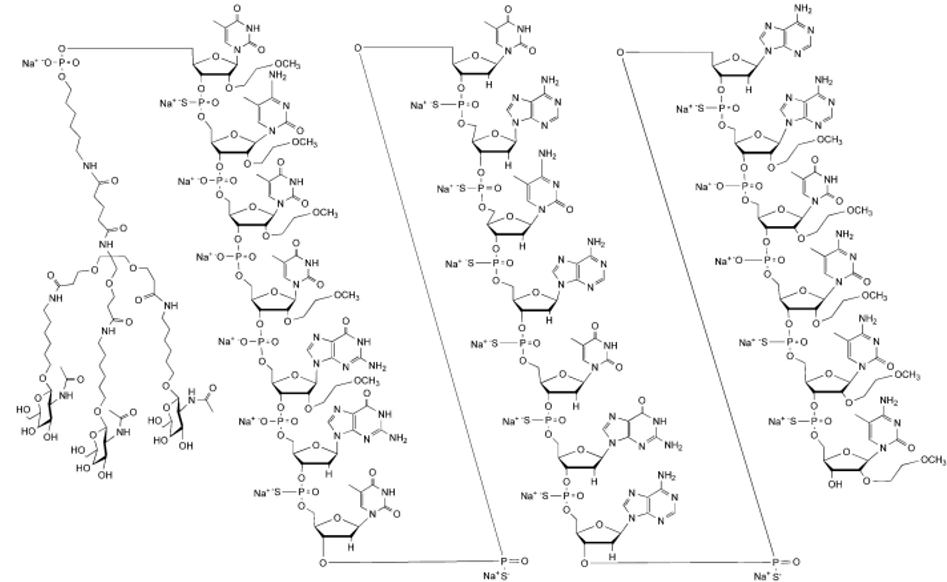
Eplontersen, Drugs.com/eplontersen | ASO | 2023.12 | Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis |
---...---
" Bio-Synthesis provides a full spectrum of high quality custom oligonucleotide modification services including 5'-triphosphate and back-bone modifications, conjugation to fatty acids, biotinylation by direct solid-phase chemical synthesis or enzyme-assisted approaches to obtain artificially modified oligonucleotides, such as BNA antisense oligonucleotides, mRNAs or siRNAs, containing a natural or modified backbone, as well as base, sugar and internucleotide linkages.
Bio-Synthesis also provides biotinylated mRNA and long circular oligonucleotides".
---...---