|
|
|
Bio-Synthesis Newsletter - September 2017
|
What is TERRA RNA?
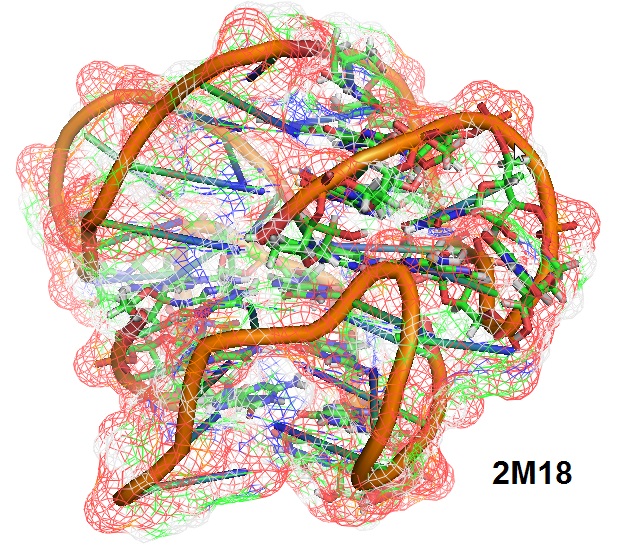 TERRA RNA refers to long noncoding telomeric repeat-containing RNAs (lnctel RNAs). TERRAs are transcribed in a regulated manner from telomeres in eukaryotes. TERRA molecules consist of chromosome end-specific subtelomeric sequences and telomeric repeats at their 3’-ends. TERRAs are a set of RNAs expressed at several distinct chromosome ends in eukaryotic cells. TERRA RNA has been implicated in telomere maintenance. However, TERRAs activities appear to be diverse, but it is thought that TERRA orchestrates different activities at chromosome ends depending on the state of the telomere. TERRA RNA refers to long noncoding telomeric repeat-containing RNAs (lnctel RNAs). TERRAs are transcribed in a regulated manner from telomeres in eukaryotes. TERRA molecules consist of chromosome end-specific subtelomeric sequences and telomeric repeats at their 3’-ends. TERRAs are a set of RNAs expressed at several distinct chromosome ends in eukaryotic cells. TERRA RNA has been implicated in telomere maintenance. However, TERRAs activities appear to be diverse, but it is thought that TERRA orchestrates different activities at chromosome ends depending on the state of the telomere.
TERRA-specific oligo probes using bridged nucleic acids (BNAs) can be used for the investigations of these diverse roles of TERRA RNAs. Human TERRA sequences containing UUAGGG repeats can form parallel-stranded G-quadruplexes. The stacking conformation of TERRAs is a potential target for drugs that recognize or induce the stacking interface.
|
|
Read More
|
|
|
What is LISH?
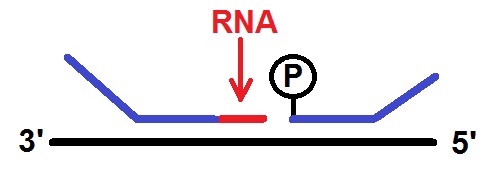 LISH refers to “Ligation in situ Hybridization.” LISH is an alternative method for the analysis of formalin fixation and paraffin embedded (FFPE) RNA. LISH refers to “Ligation in situ Hybridization.” LISH is an alternative method for the analysis of formalin fixation and paraffin embedded (FFPE) RNA.
LISH uses T5 RNA Ligase 2 to join adjacent chimeric RNA-DNA probe pairs hybridized in situ in fixed RNA target sequences. The novel LISH analysis method has broad applications ranging from multiplexed gene expression to sensitive detection of infectious pathogens.
LISH works by hybridization of pairs of chimeric 3′-diribonucleotide-containing and 5′-phosphorylated DNA probes on formalin fixed RNA within a tissue section. For LISH to work, adjacently annealed probe pairs are ligated in situ with Rnl2, followed by RNase H treatment releasing RNA-templated ligation products into solution for downstream analysis and destroying unwanted DNA-templated ligation products. In the last step ligation products are amplified by multiplex PCR using universal ‘outside’ primers, ‘OF’ and ‘OR’.
|
|
Read More
|
|
|
DNA-protein conjugates!
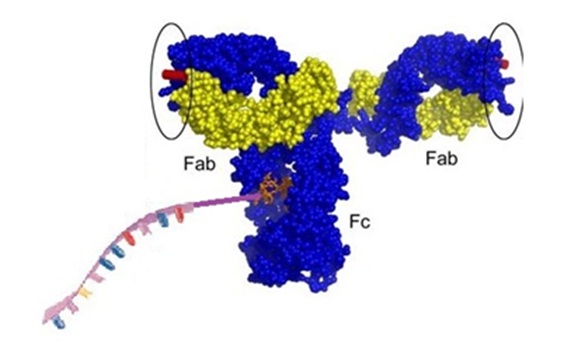 DNA-protein or DNA-enzyme conjugates are molecular tools used in bioanalytical chemistry and molecular diagnostics as well as in nanotechnology. DNA conjugates are unique molecules allowing functionalization of proteins or peptides for identification or manipulating purposes. For immunization approaches, DNA oligonucleotides can be conjugated to proteins or adjuvants. DNA-antibody conjugates are useful for specific and sensitive detection methods such as immune-PCR or hybridization based methods. The immuno-PCR approach combines specific target detection with the sensitivity of PCR-based quantification. DNA conjugates can be synthesized using selective cross-linking chemistries. A variety of functional groups such as enzymes, fluorophores, small molecules, pH sensors, or other reporter groups can also be added to DNA-conjugates. Also, DNA-conjugates can be used as biosensors or for the detection of single molecules making oligonucleotide-conjugates a versatile group of biomolecules. DNA-protein or DNA-enzyme conjugates are molecular tools used in bioanalytical chemistry and molecular diagnostics as well as in nanotechnology. DNA conjugates are unique molecules allowing functionalization of proteins or peptides for identification or manipulating purposes. For immunization approaches, DNA oligonucleotides can be conjugated to proteins or adjuvants. DNA-antibody conjugates are useful for specific and sensitive detection methods such as immune-PCR or hybridization based methods. The immuno-PCR approach combines specific target detection with the sensitivity of PCR-based quantification. DNA conjugates can be synthesized using selective cross-linking chemistries. A variety of functional groups such as enzymes, fluorophores, small molecules, pH sensors, or other reporter groups can also be added to DNA-conjugates. Also, DNA-conjugates can be used as biosensors or for the detection of single molecules making oligonucleotide-conjugates a versatile group of biomolecules.
|
|
Read More
|
|
|
A cyclic peptide blocks cancer!
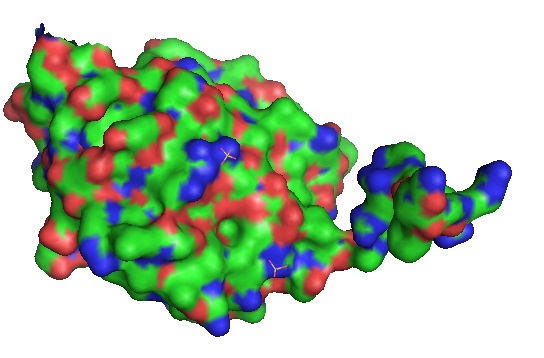 Owens et al. recently designed a macrocyclic peptide that acts as an inhibitor of the hedgehog signaling pathway. The research group designed a genetically encoded cyclic peptide based on the sonic hedgehog-binding loop of hedgehog-interacting protein. Using a library of cyclic peptides, the researchers screened for hedgehog inhibitor peptides. Doing so, a peptide that suppresses activation of the hedgehog signaling pathway in living cells was identified. Owens et al. recently designed a macrocyclic peptide that acts as an inhibitor of the hedgehog signaling pathway. The research group designed a genetically encoded cyclic peptide based on the sonic hedgehog-binding loop of hedgehog-interacting protein. Using a library of cyclic peptides, the researchers screened for hedgehog inhibitor peptides. Doing so, a peptide that suppresses activation of the hedgehog signaling pathway in living cells was identified.
The hedgehog signaling pathway is important for proper development and cell differentiation during embryonic development. Hedgehog signaling is critical for the development of embryonic systems, therefore, its expression is tightly regulated by transcription factors. The aberrant activation of this pathway is thought to lead to the development and progression of several human cancers.
|
|
Read More
|
|
|
|
|
Bio-Synthesis, Inc.
800 Mario Court, Lewisville, TX 75057, USA
Toll Free: 800.227.0627 | 1.972.420.8505 (Intl.)
|
|
|
|
|
|