|
|
|
Bio-Synthesis Newsletter - October 2017
|
BNA- and Biotin-oligonucleotides as affinity probes for protein-RNA complexes!
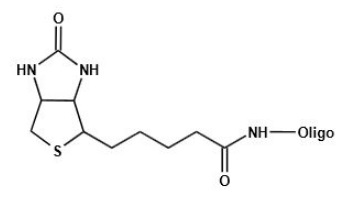 Large intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) are now emerging as key regulators of diverse cellular processes. However, determining the function of individual lincRNAs is very challenging. Tens of thousands of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been already discovered in eukaryotes, but their functions are mostly unknown. For studying their function have been and are constantly developed. An example is the RNA-pull down assay. For the assay to work, lncRNA probes labeled with high-affinity tags such as fluorophores, bridged nucleic acids (BNAs), biotin or biotin labeled with stable isotopes are needed. Large intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) are now emerging as key regulators of diverse cellular processes. However, determining the function of individual lincRNAs is very challenging. Tens of thousands of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been already discovered in eukaryotes, but their functions are mostly unknown. For studying their function have been and are constantly developed. An example is the RNA-pull down assay. For the assay to work, lncRNA probes labeled with high-affinity tags such as fluorophores, bridged nucleic acids (BNAs), biotin or biotin labeled with stable isotopes are needed.
|
|
Read More
|
|
|
Oligopeptide-proton symporters use proton gradients to transport peptides
 The symporter proteins pepT1 and PepT2 are major transporter membrane proteins that use a proton gradient for the uptake of di-and tri-peptides in the small intestine and kidney. In general, symporter proteins are integral membrane proteins that transport many different molecule types across the cell membrane. Crystal structure analysis of the pepTSo protein allowed the location of the peptide-binding site in the central hydrophilic cavity of the transporter protein. Also, residues involved in proton coupling were identified. PepT1 is a high-capacity, low-affinity transporter that provides the main route for dietary peptide uptake. However, PepT2 operates as a low-capacity, high-affinity transporter mediating more selective transport in the kidney and other tissues. In humans, transport proteins transport a broad spectrum of orally administered drugs, such as the β-lactam antibiotics, antivirals such as valacyclovir, and the vasopressor midodrine. The symporter proteins pepT1 and PepT2 are major transporter membrane proteins that use a proton gradient for the uptake of di-and tri-peptides in the small intestine and kidney. In general, symporter proteins are integral membrane proteins that transport many different molecule types across the cell membrane. Crystal structure analysis of the pepTSo protein allowed the location of the peptide-binding site in the central hydrophilic cavity of the transporter protein. Also, residues involved in proton coupling were identified. PepT1 is a high-capacity, low-affinity transporter that provides the main route for dietary peptide uptake. However, PepT2 operates as a low-capacity, high-affinity transporter mediating more selective transport in the kidney and other tissues. In humans, transport proteins transport a broad spectrum of orally administered drugs, such as the β-lactam antibiotics, antivirals such as valacyclovir, and the vasopressor midodrine.
|
|
Read More
|
|
|
Vitamin C is a regulator for stem cells and cancer
 Since 1969 we know that vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, has anticancer effects. It has long been observed that severe deficiency of vitamin C causes the lethal disease scurvy, a condition well known to many early sailors. More recently, a new previously unknown role for vitamin C has been discovered in stem cell biology. It was observed that high levels of vitamin C in blood-forming stem cells influence the number and function of the cells. Vitamin C affects the development of leukemia through binding to a tumor-suppressor protein. New research now revealed that vitamin C regulates the number and function of blood-forming hematopoietic stem cells. Vitamin C was found to be a cofactor of the enzyme Tet2. Ten-eleven Translocation (TET) enzymes regulate the epigenetic methylation of DNA. Tet2 mutations are known to be a common cause for myeloid leukemia in humans. TET2 is one of the three proteins of the TET family. These proteins are evolutionarily conserved dioxygenases catalyzing the conversion of 5-methyl-cytosine (5-mC) to 5-hydroxymethyl-cytosine (5-hmC) and promote DNA demethylation. Vitamin C deficiency alters hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) function and may influence the risk of diseases such as leukemia. Since 1969 we know that vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, has anticancer effects. It has long been observed that severe deficiency of vitamin C causes the lethal disease scurvy, a condition well known to many early sailors. More recently, a new previously unknown role for vitamin C has been discovered in stem cell biology. It was observed that high levels of vitamin C in blood-forming stem cells influence the number and function of the cells. Vitamin C affects the development of leukemia through binding to a tumor-suppressor protein. New research now revealed that vitamin C regulates the number and function of blood-forming hematopoietic stem cells. Vitamin C was found to be a cofactor of the enzyme Tet2. Ten-eleven Translocation (TET) enzymes regulate the epigenetic methylation of DNA. Tet2 mutations are known to be a common cause for myeloid leukemia in humans. TET2 is one of the three proteins of the TET family. These proteins are evolutionarily conserved dioxygenases catalyzing the conversion of 5-methyl-cytosine (5-mC) to 5-hydroxymethyl-cytosine (5-hmC) and promote DNA demethylation. Vitamin C deficiency alters hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) function and may influence the risk of diseases such as leukemia.
|
|
Read More
|
|
|
A new nucleoside analog inhibits bacterial RNA polymerase.
 A new antibacterial compound called pseudouridinmycin (PUM) has been recently discovered using a conventional microbial extract screening approach. Chellat and Riedl in 2017 reported that this broad-spectrum nucleoside-analogue inhibitor called pseudouridimycin is selective for bacterial RNA polymerase and shows very low resistance rates. PUM consist of a formamidinylated, N-hydroxylated Gly-Gln dipeptide conjugated to 6'-amino-pseudouridine. Since emerging drug-resistant bacterial pathogens are responsible for a new public health crisis, it is good to know that new antibacterial drugs may be available soon. A new antibacterial compound called pseudouridinmycin (PUM) has been recently discovered using a conventional microbial extract screening approach. Chellat and Riedl in 2017 reported that this broad-spectrum nucleoside-analogue inhibitor called pseudouridimycin is selective for bacterial RNA polymerase and shows very low resistance rates. PUM consist of a formamidinylated, N-hydroxylated Gly-Gln dipeptide conjugated to 6'-amino-pseudouridine. Since emerging drug-resistant bacterial pathogens are responsible for a new public health crisis, it is good to know that new antibacterial drugs may be available soon.
|
|
Read More
|
|
|
|
|
Bio-Synthesis, Inc.
800 Mario Court, Lewisville, TX 75057, USA
Toll Free: 800.227.0627 | 1.972.420.8505 (Intl.)
|
|
|
|
|
|